Contributing to the reduction of GHG emissions through energy-saving measures in the flat glass manufacturing line
AGC Inc. Yokohama Technical Center(Tsurumi Ward, Yokohama)

(Research collaborator)CARBON FREE CONSULTING CORPORATION(Naka Ward, Yokohama)

1 Business
Introduction of energy-efficient melting furnaces for flat glass in Indonesia using the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
2 Country, region (city, etc.)
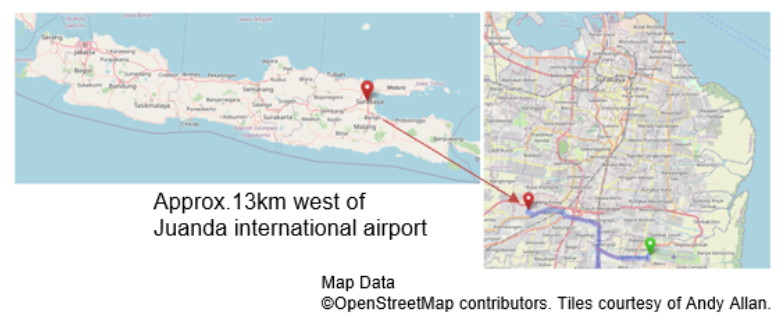
Indonesia (Sidoarjo)
3 Contribution to SDGs


4 Project Results
Contributing to the reduction of GHG emissions in Indonesia through energy-saving measures in the company’s manufacturing line
In 2021, Indonesia announced a carbon-neutral target to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2060 at the latest. While the global target is set for 2050, this is an ambitious goal for Indonesia, advancing the previous target of 2070 by 10 years. However, considering Indonesia’s expected population growth, urban development, and increased energy demand, international support will be essential for achieving the country’s long-term goal.
The AGC Group has set intermediate goals for carbon neutrality by 2050, including a 30% reduction in GHG emissions and a 50% reduction in GHG emissions per unit of sales by 2030. Among these, GHG emissions in the melting process of flat glass manufacturing account for a significant portion of the group’s total emissions, and are positioned as one of the priority areas to be addressed.
As of March 2024, the AGC Group owns four manufacturing lines for architectural and automotive glass in Indonesia. In the flat glass manufacturing process, a significant amount of fossil fuel is consumed, primarily in the melting process of raw materials (sand, soda ash, dolomite, etc.). Therefore, energy-saving measures in the manufacturing lines align with the company’s GHG reduction goals and contribute to achieving Indonesia’s targets.
To promote energy-saving measures for the manufacturing lines in Indonesia, a feasibility study was conducted in the 2022 fiscal year. In the 2023 fiscal year, the project was selected for the equipment subsidy program under the Ministry of the Environment’s Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) funding support, leading to the introduction of an energy-efficient glass melting furnace.
【Project location】
Conducting a feasibility study in collaboration with the City of Yokohama and local companies
AGC’s connection with Yokohama dates back over 100 years. In 1916, AGC established the AGC Yokohama Technical Center (formerly Keihin Factory) in the heart of the Keihin coastal industrial area, Tsurumi Ward in Yokohama. In 2021, by utilizing the support provided by Yokohama City’s Business Location Promotion Incentive Program, AGC consolidated various development functions that had been scattered throughout the city, making the Yokohama Technical Center the central hub for AGC’s technology development. Additionally, the center manufactures flat glass used in construction and automotive display cover glass, and with its unique capability to handle every step from research to production and shipment, it has played a central role in the feasibility study and in the JCM equipment subsidy application.

AGC has participated in networking opportunities such as the Y-PORT workshops hosted by the City of Yokohama, as well as business matching seminars in Cebu (Philippines), Da Nang (Vietnam), and Batam (Indonesia). Through these networking opportunities, AGC collaborated with the City of Yokohama and local companies to conduct a feasibility study for energy-saving measures on the manufacturing lines in Indonesia.
The person responsible for this project at AGC reflects on the process, saying, ‘Through participating in Y-PORT events and other activities, I was aware that the City of Yokohama had been involved in various initiatives in Indonesia. It was also important to have the GHG reduction effects objectively evaluated by a third party. While looking for a partner, I was able to connect with Carbon Free Consulting Corporation, a YUSA (Yokohama Urban Solution Alliance) member company, through the Y-PORT Center’s network.’ In the feasibility study, the project utilized subsidies from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry and focused on the following main areas: 1) translating the detailed business plan into action and conducting an economic evaluation, 2) preliminary consultations with the Indonesia JCM Secretariat, and 3) clarifying the GHG reduction effects. Particularly, item 3 was handled by Carbon Free Consulting Corporation, a Yokohama-based company.

Expectations on GHG emission reductions in the global supply chain and in the countries of operation
This project in Indonesia aims to improve energy efficiency by 1) changing the combustion method and 2) modifying the furnace structure, in line with the scheduled refurbishment (cold repair) of the AGC Group’s flat glass melting furnaces. Compared to the previous system, an estimated reduction of approximately 5,700 tCO2/year in GHG emissions is expected. The lifespan of flat glass melting furnaces is approximately 10 to 15 years, and in the future, energy-saving measures and the introduction of new technologies are being considered for cold repairs and refurbishments of other manufacturing lines in Asia (such as in Indonesia and Thailand) operated by the AGC Group.
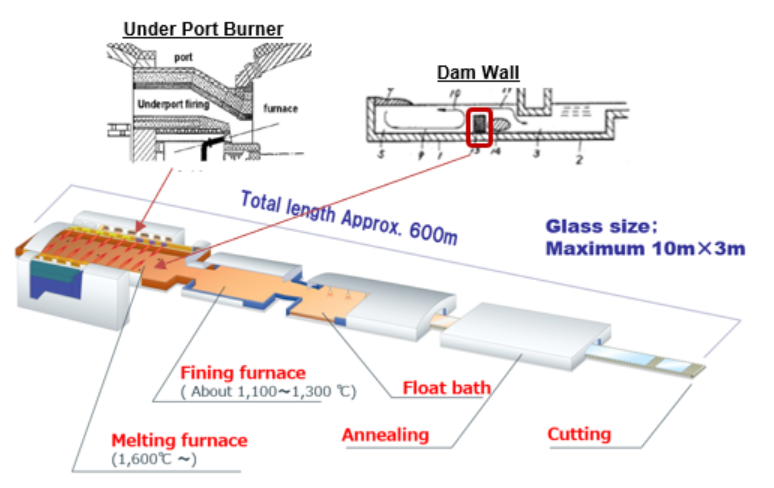
As of March 2024, the AGC Group operates four glass manufacturing lines for architectural and automotive glass in Japan and seven lines in Asia, including four in Indonesia. Moving forward, the company expects to reduce GHG emissions in its global supply chain and in the countries where it operates by continuing to promote energy-saving and decarbonization measures in the manufacturing processes.
